How are the Internal and External Camera Parameters defined? -PIX4Dmatic
This article describes in detail the mathematical models behind the camera's internal and external parameters for PIX4Dmatic
IN THIS ARTICLE
Camera external parameters
Camera internal parameters
Perspective lens
Camera without distortion model
Camera with distortion model
Fisheye lens
The external camera parameters are different for each image. They are given by:
- T = (Tx, Ty, Tz) the position of the camera projection center in world coordinate system.
- R the rotation matrix that defines the camera orientation with angles ω, φ, κ (PATB convention).

If X = (X, Y, Z) is a 3D point in world coordinate system, its position X' = (X', Y', Z') in camera coordinate system is given by:
![]()
The pixel coordinate (xu, yu) of the 3D point projection without distortion model is given by:

Where f is the focal length in pixel, and (cx, cy) the principal point in pixel coordinates.
Let:
![]()
be the homogeneous point,
![]()
the squared 2D radius from the optical center, R1, R2, R3 the radial and T1, T2 the tangential
distortion coefficients. The distorted homogeneous point in camera coordinate system (xhd, yhd)
is given by:

The pixel coordinate (xd, yd) of the 3D point projection with distortion model is given by:

Where f is the focal length in pixel, and (cx, cy) the principal point in pixel coordinates.
The distortion for a fisheye lens is defined by:
- The parameters C, D, E, F that describe an affine deformation of the circular image in
pixel coordinates.
The diagonal elements of the affine matrix can be related to the focal length f:
The off-diagonal elements are connected to the distortion of the projected image circle,
which, in the most general case, can be a rotated ellipse. - The coefficients p2, p3, p4 of a polynomial:

Where:
The pixel coordinate (xd, yd) of the 3D point projection with a fisheye distortion model is
given by
![]()
Where:

And (cx, cy) is the principal point in pixel coordinates.
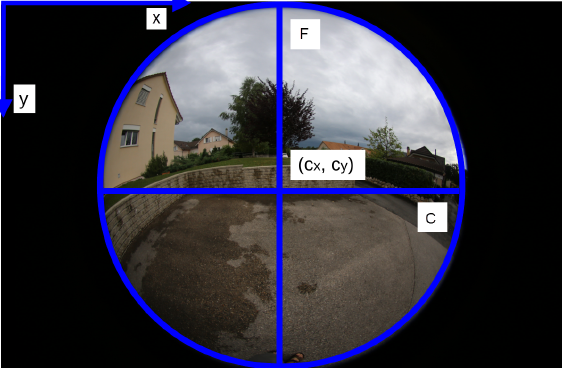
When using an 8mm Sigma lens on a Canon 6D camera with an image size of 5472 x 3648 pixel(figure. 3), the internal parameters can be initialized as follows:
- (cx, cy) = ( 5472/2, 3648/2 ) pixel is the center of the projected image circle
- p2 = p3 = p4 = 0
- p1 = 1
- C = F = 1780 pixel is the radius of the image circle
- E = D = 0