Internal Camera Parameters Correlation - PIX4Dmapper
The internal camera parameters define the geometries of the camera’s lens and sensor;
or how light passes through the camera’s lens and hits the camera’s sensor.
The correlation between the internal camera parameters describes how much these parameters relate to each other, meaning how a change in one affects the others.
Ideally, the internal parameters should be independent, especially when characterizing the interior orientation of a new camera. However, having some correlation between parameters is expected or can even be helpful in detecting certain types of problems.
Correlation between the camera parameters might occur in projects with:
- Uniform data such as: flat terrain relative to flight heights, GCPs placed in one plane (no height variations), few ATPs/MTPs/GCPs at the edges of the images, all images taken with the same orientation.
- Nadir images, in which correlation between the radial distortion parameters and between the 2 principal point coordinates might occur.
- Oblique images, in which correlation between the focal length and the coordinates of the principal point and between the coordinates of the principal point and the tangential distortion parameters might occur.
In the Quality Report the correlation values are represented by shades of grey. The darker the color, the smaller the correlation between the parameters.
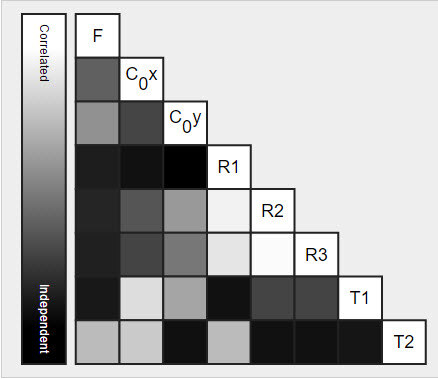
The following help with decorrelation:
- Accurate camera positions (e.g. RTK, or at least GPS), combined with GCPs.
- Terrain depth variations.
- MTPs at multiple depths and near image edges for oblique projects: How to import and mark Manual Tie Points (MTPs).
- Different camera orientations (eg. rotate at ends of grid rows, so images will be at 180°).
- Using All Prior for the internal parameters optimization: Menu Process > Processing Options... > 1. Initial Processing > Calibration.
Having the leading parameters (the focal length (F) and the coordinates of the principal point (c0x, c0y)) highly correlated can be an indicator of a problem with the reconstruction. In this case, it is recommended to process the first step of processing with the All Prior option for the Internal Parameters Optimization: Menu Process > Processing Options... > 1. Initial Processing > Calibration.
